Following is the basic window which you get when you start word application. Let us understand various important parts of this window.
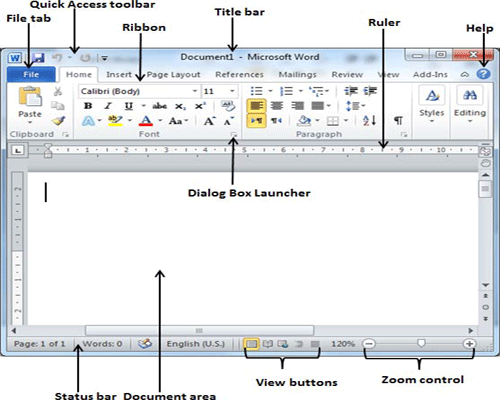
File Tab:
The File tab replaces the Office button from Word 2007. You can click it to check Backstage view, which is the place to come when you need to open or save files, create new documents, print a document, and do other file-related operations.
Quick Access Toolbar:
This you will find just above the File tab and its purpose is to provide a convenient resting place for the Word most frequently used commands. You can customize this toolbar based on your comfort.
Ribbon:
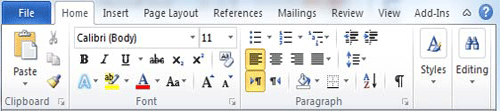
Ribbon contains commands organized in three components:
Tabs: They appear across the top of the Ribbon and contain groups of related commands. Home, Insert, Page Layout are example of ribbon tabs.
Groups: They organize related commands; each group name appears below the group on the Ribbon. For example group of commands related to fonts or or group of commands related to alignment etc.
Commands: Commands appear within each group as mentioned above.
Title bar:
This lies in the middle and at the top or the window. Title bar shows the program and document titles.
Rulers:
Word has two rulers - a horizontal ruler and a vertical ruler. The horizontal ruler appears just beneath the Ribbon and is used to set margins and tab stops. The vertical ruler appears on the left edge of the Word window and is used to gauge the vertical position of elements on the page.
Help:
The Help Icon can be used to get word related help anytime you like. This provides nice tutorial on various subjects related to word.
Zoom Control:
Zoom control lets you zoom in for a closer look at your text. The zoom control consists of a slider that you can slide left or right to zoom in or out, . and + buttons you can click to increase or decrease the zoom factor.
View Buttons:
The group of five buttons located to the left of the Zoom control, near the bottom of the screen, lets you switch among Word's various document views.
Print Layout view: This displays pages exactly as they will appear when printed.
Full Screen Reading view: This gives a full screen look of the document.
Web Layout view: This shows how a document appears when viewed by a Web browser, such as Internet Explorer.
Outline view: This lets you work with outlines established using Word.s standard heading styles.
Draft view: This formats text as it appears on the printed page with a few exceptions. For example, headers and footers aren't shown. Most people prefer this mode.
Document Area:
The area where you type. The flashing vertical bar is called the insertion point and it represents the location where text will appear when you type.
Status Bar:
This displays document information as well as the insertion point location. From left to right, this bar contains the total number of pages and words in the document, language etc.
You can configure the status bar by right-clicking anywhere on it and by selecting or deselecting options from the provided list.
Dialog Box Launcher:
This appears as very small arrow in the lower-right corner of many groups on the Ribbon. Clicking this button opens a dialog box or task pane that provides more options about the group.

